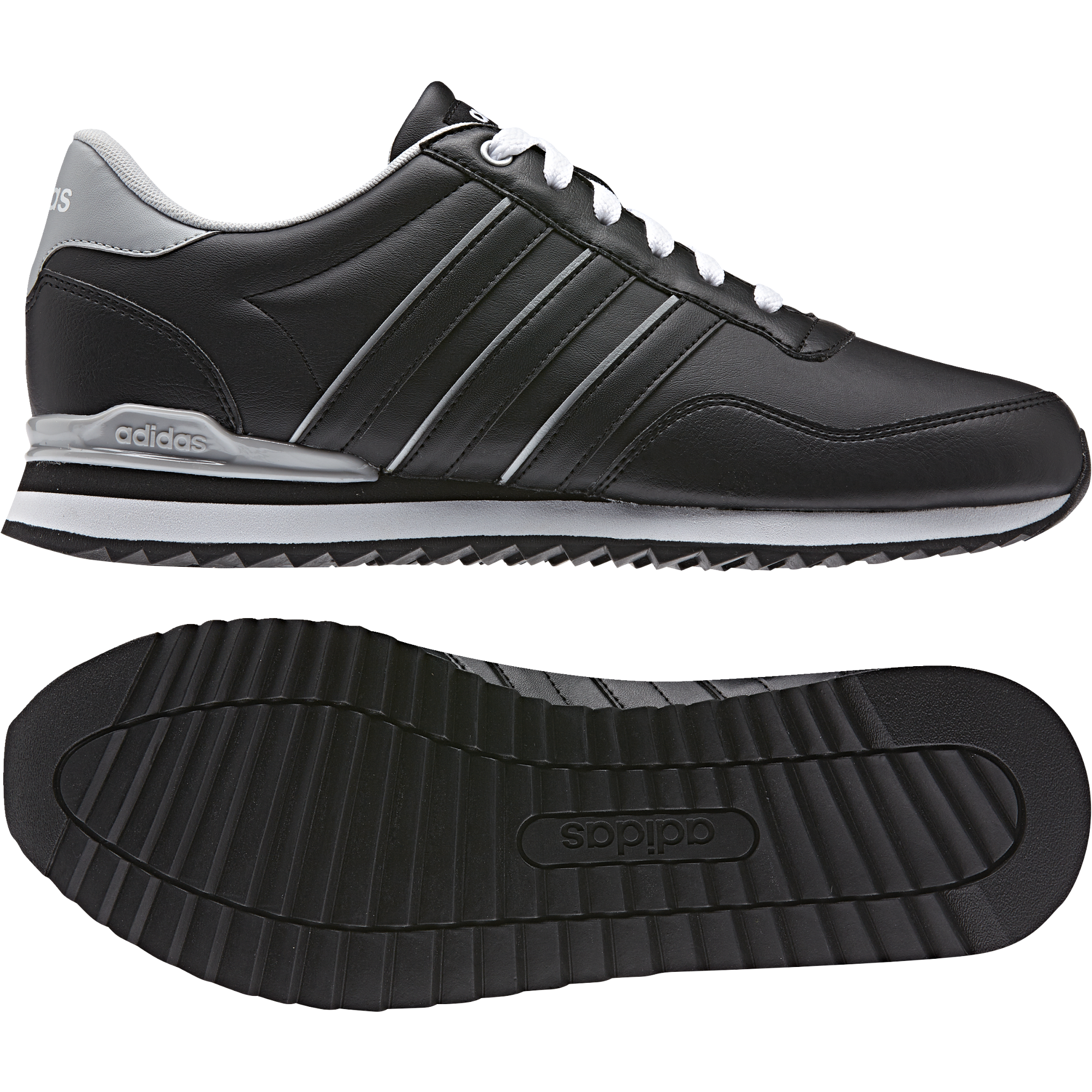
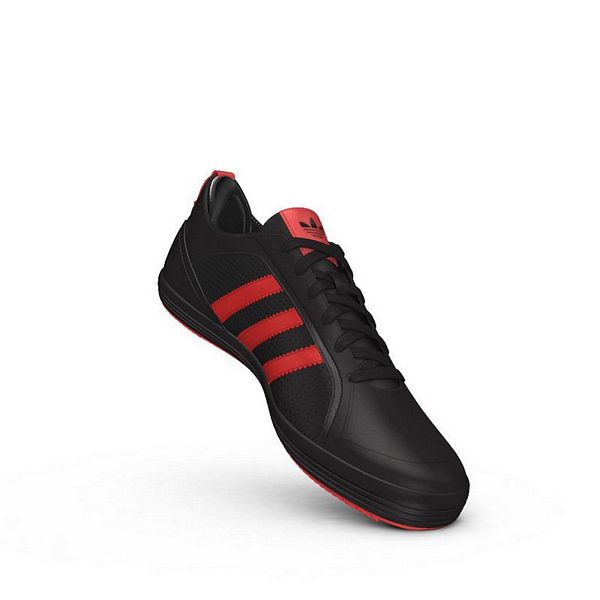
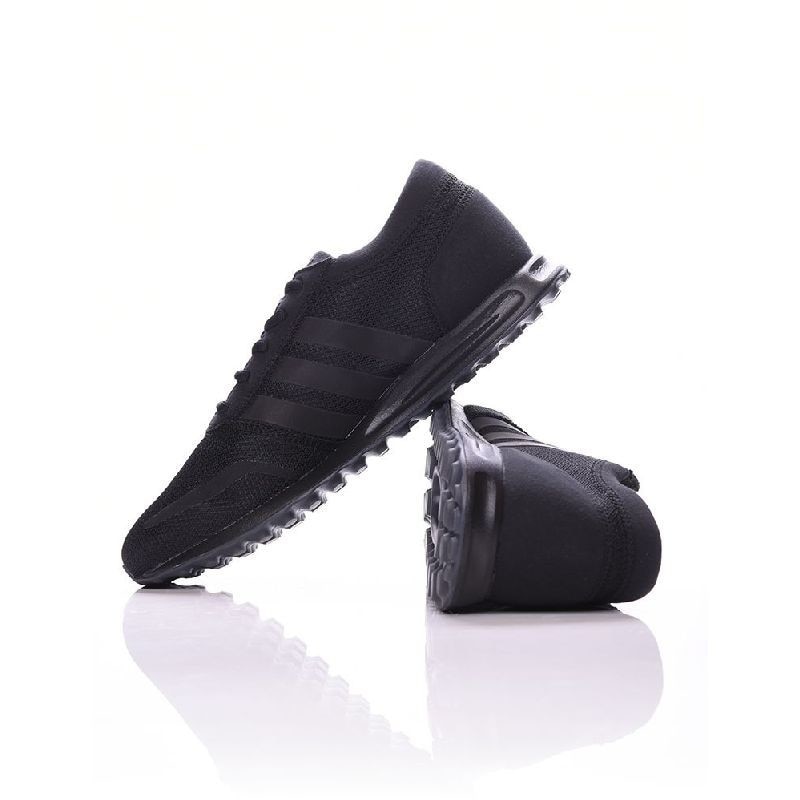
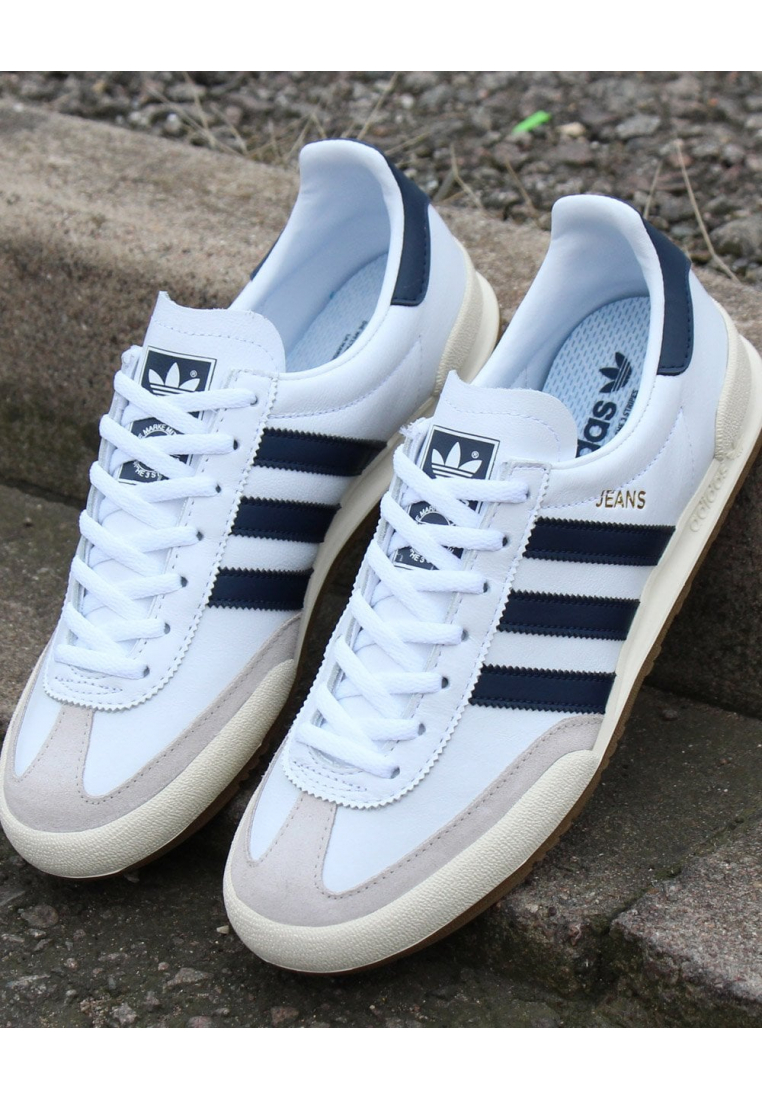
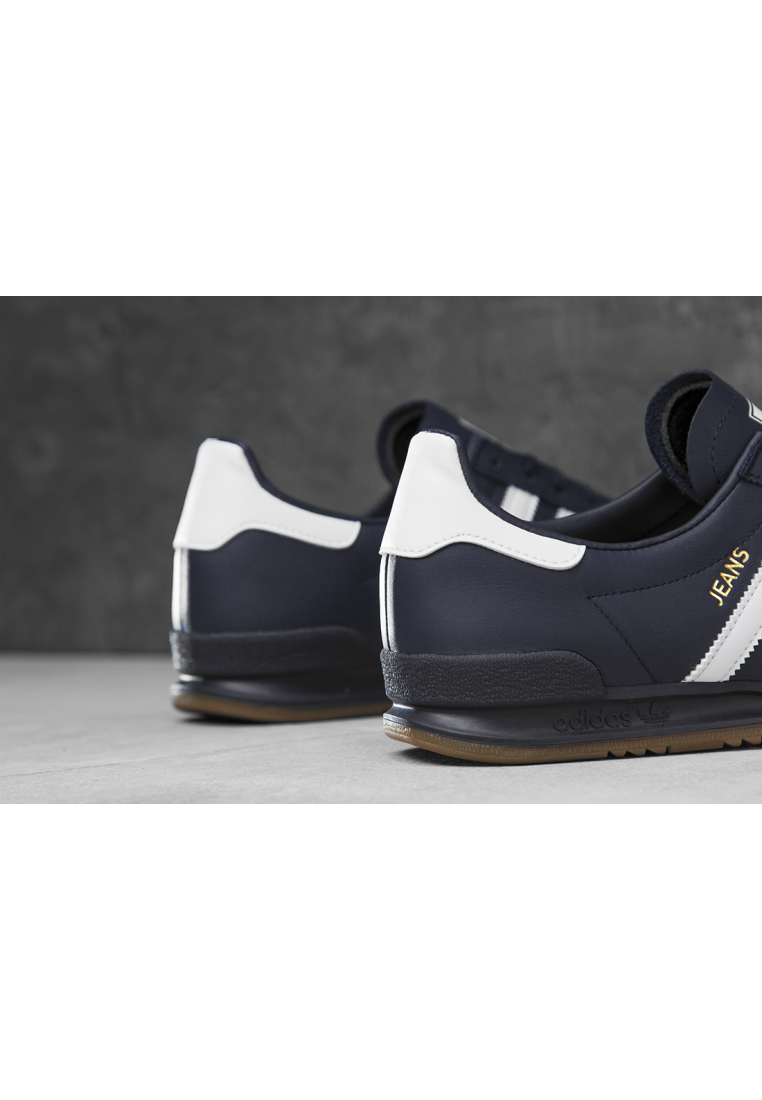
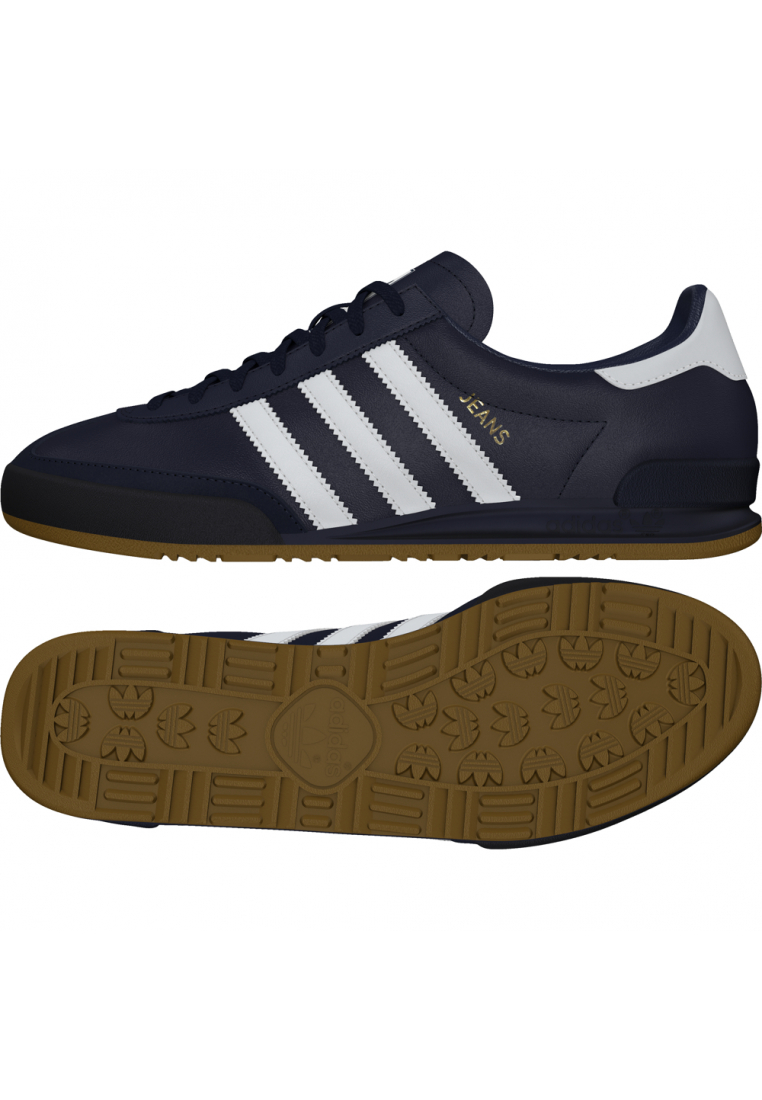
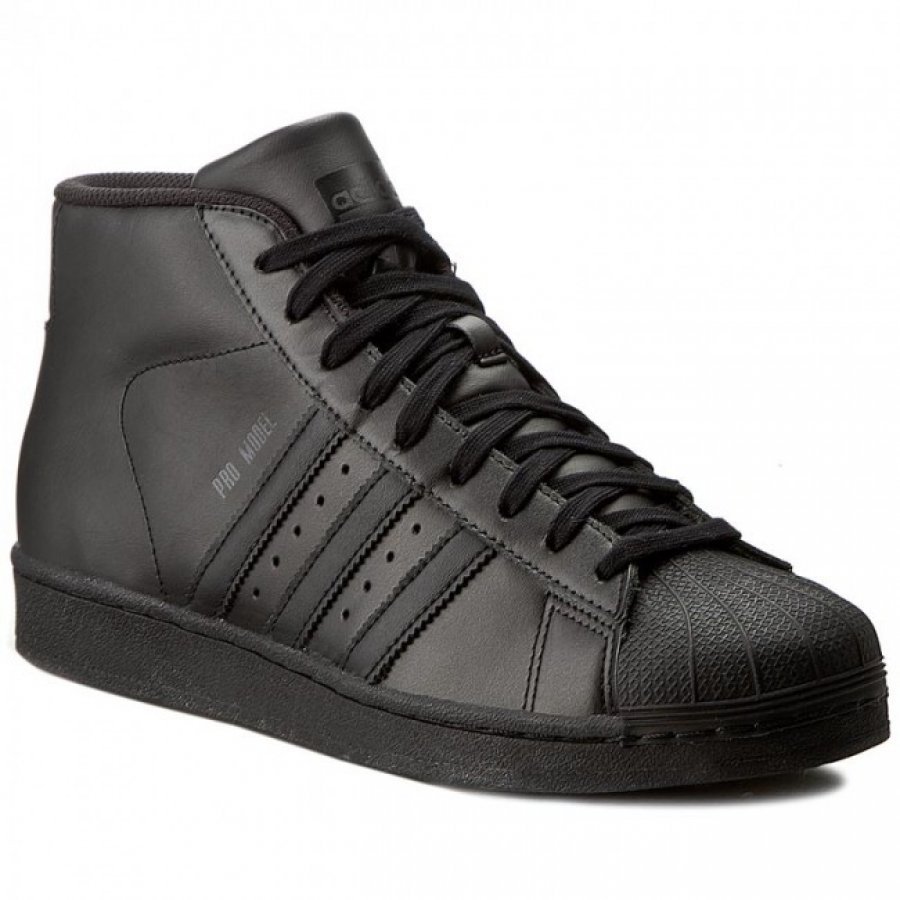
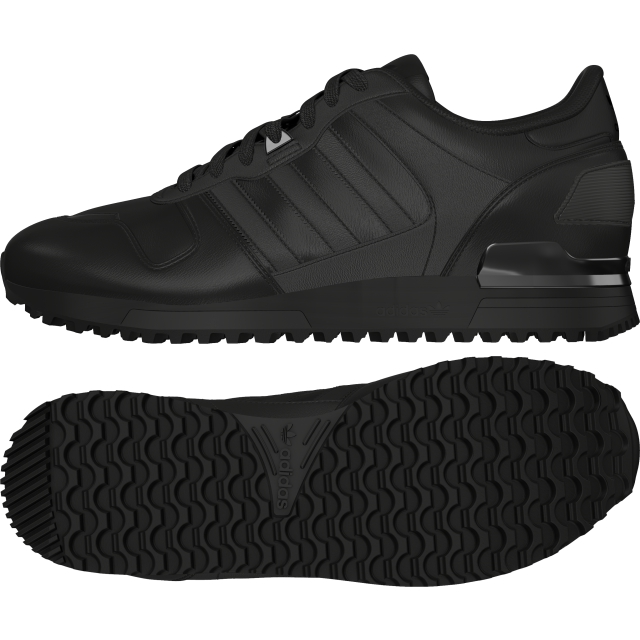
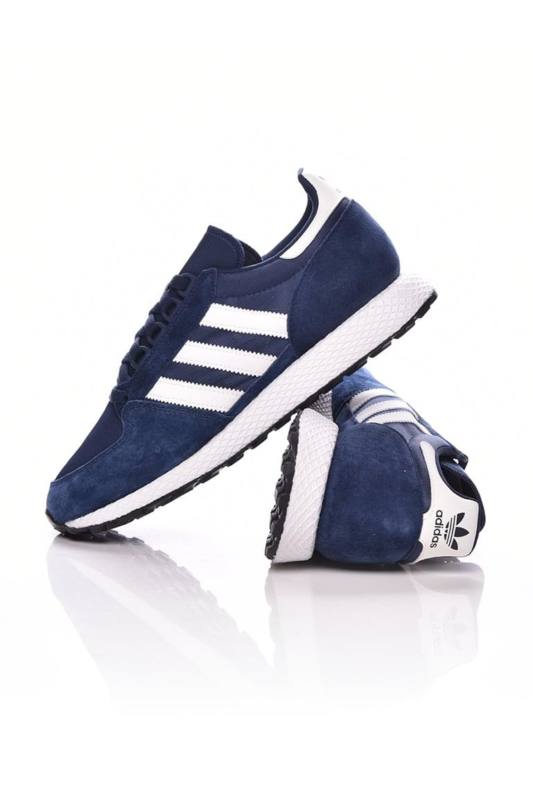
Adidas Jogger Cl férfi utcai cipő , Férfi cipő | utcai cipő | adidas_neo | Adidas Jogger Cl férfi utcai cipő
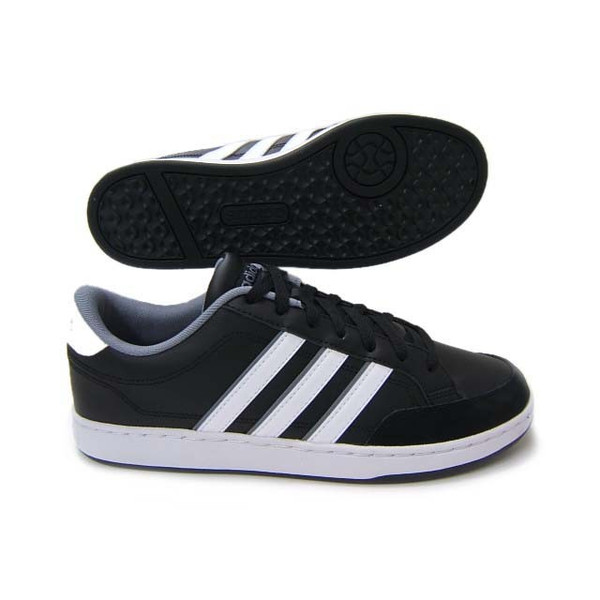

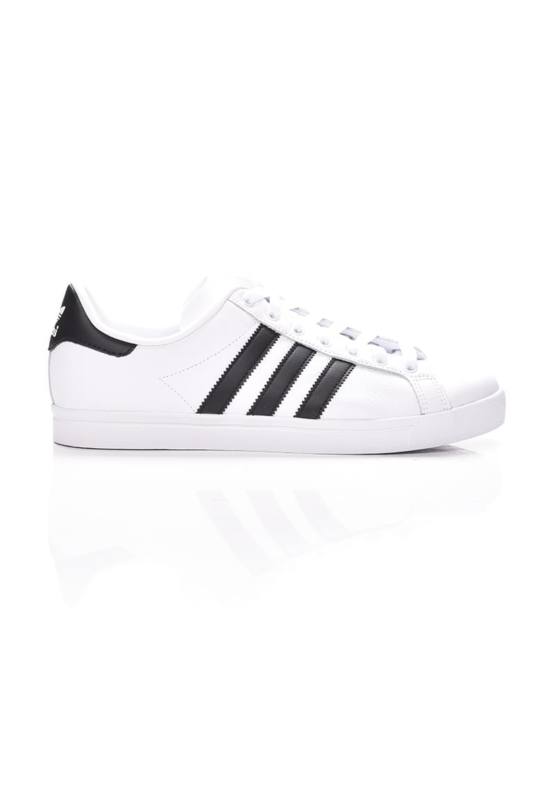
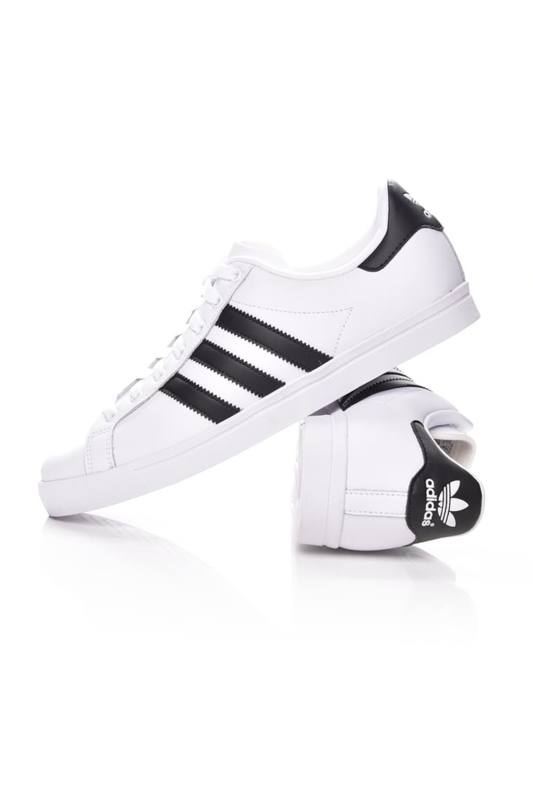
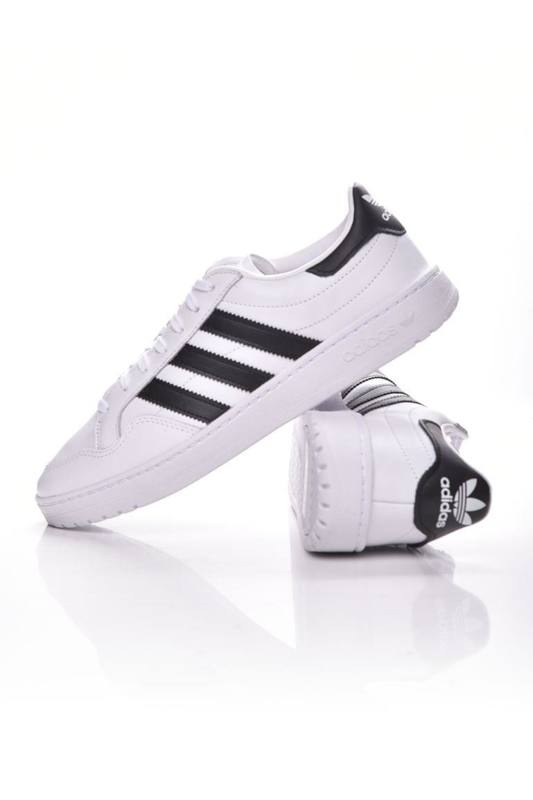
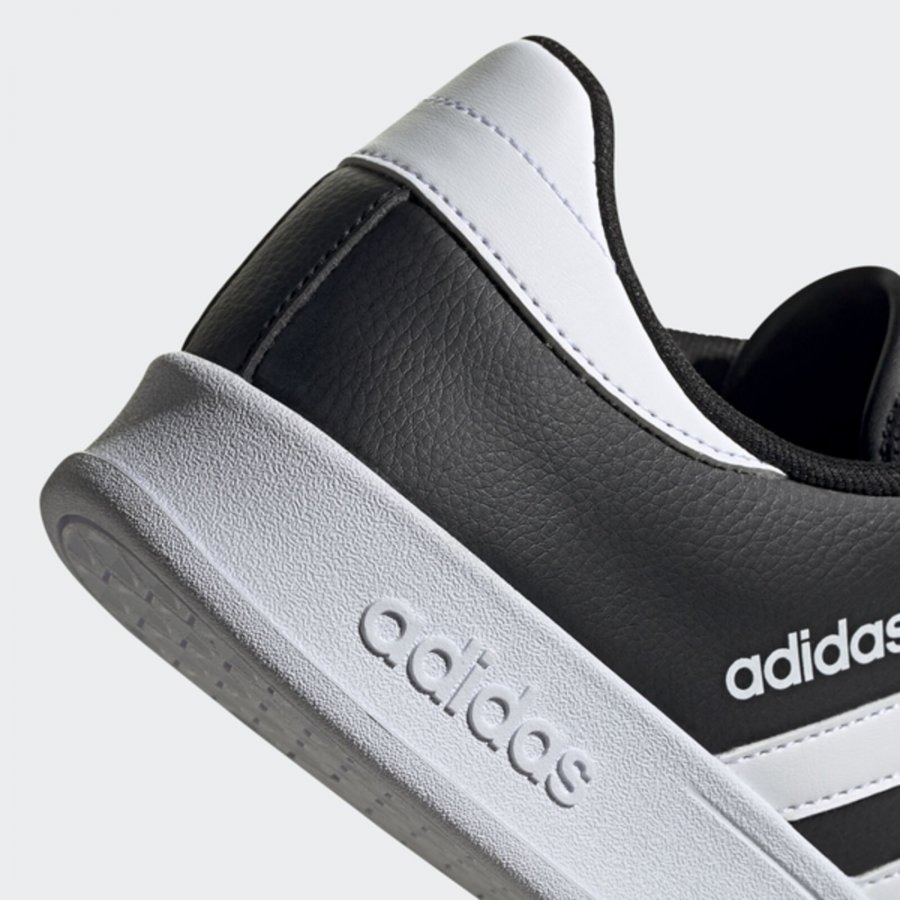
Adidas Courtset férfi utcai cipő , Férfi cipő | utcai cipő | adidas_neo | Adidas Courtset férfi utcai cipő
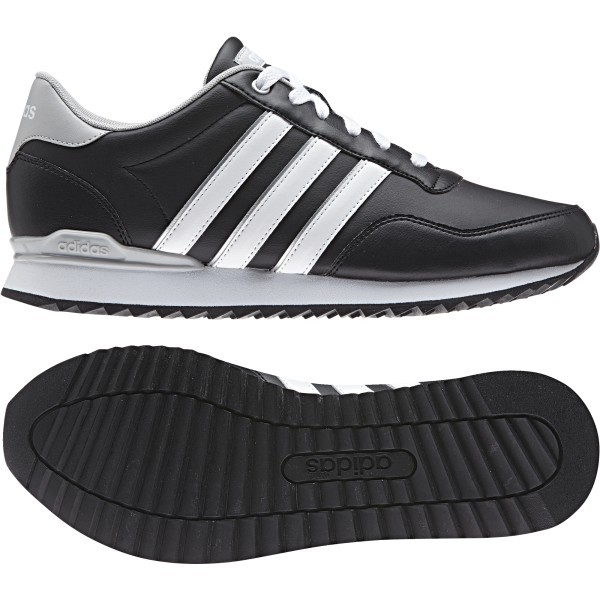

Adidas Jogger Cl férfi utcai cipő , Férfi cipő | utcai cipő , ferfi , Adidas Jogger Cl férfi utcai cipő