Magas nedvszívóképességű higiéniai alátét - kutyapelenka 100 darab, ajándék 30 darab tasakkal - eMAG.hu

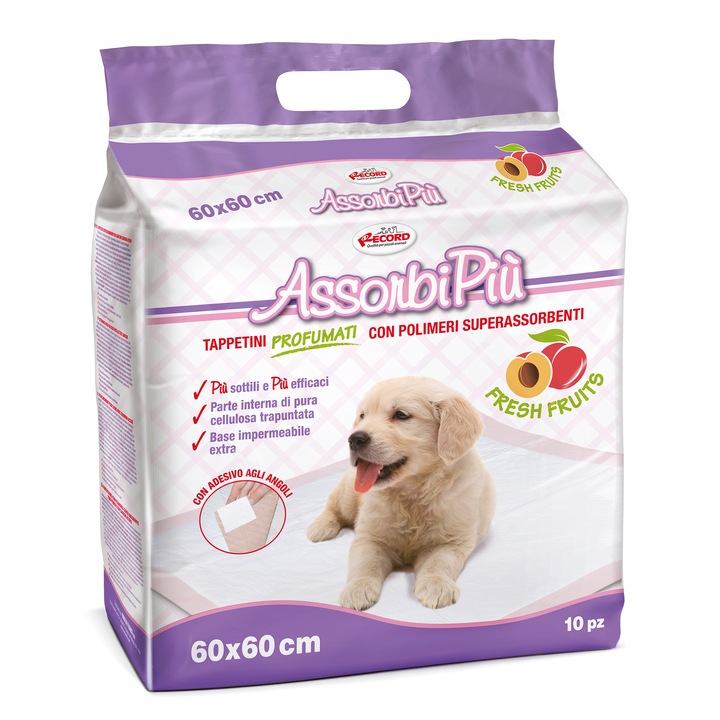
Kutyapelenka nedvszívó alátét 60x60cm, 10 darab | Háztartási eszközök, találmányok és ajándékok a Parforintert.hu webáruházból
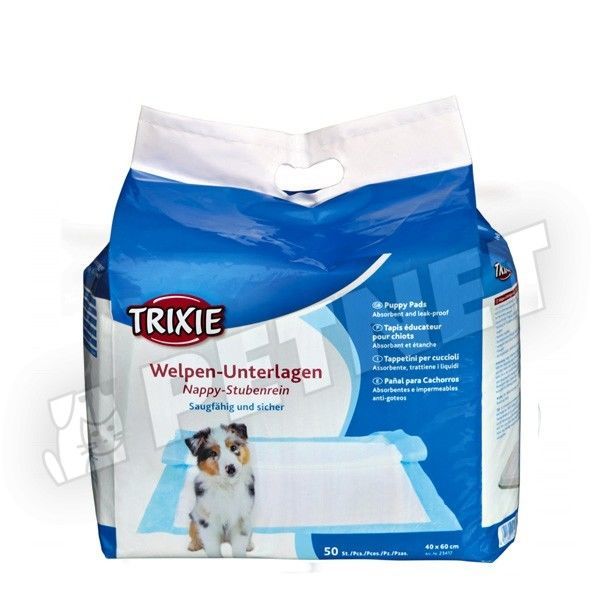

Trixie Nappy helyhez szoktató pelenka 60x40cm 7db - Szobatisztaságra nevelő kutyapelenka - 20% kedvezmény